Storage of Bluetooth Link keys
BR/EDR
BLE
The pairing process concludes with the establishment of a link key between the devices that both must keep authenticating and encrypt future connections.
The storage of these link keys can be critical to maintain confidentiality in Bluetooth connections, so their storage must be secure. On Linux systems, it is common for them to be stored in clear files protected by access permissions. this protection may not be sufficient on a device without encrypted storage: an attacker can access the stored data, extract the keys, and use them if they are valid to communicate with the other end.
In small devices or devices with proprietary implementations (Bluetooth headsets and speakers, for example), this storage may be defined by the manufacturer and the confidentiality of the keys must be verified by reversing techniques or by accessing the device’s firmware.
Description
Verifying that key confidentiality is protected requires knowledge of the device software and the presence of TPM chips.
On devices with standard operating systems, it will be possible to use the tools available. in the case of Linux systems, the BlueZ stack stores the link keys in plain text files that can usually be found in /var/lib/bluetooth. Android also stores bluetooth keys in /data/misc/bluedroid/bt_config.conf in a plaintext format. Windows uses the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\BTHPORT\Parameters\Keys\.
For devices with proprietary firmware, it may be necessary to extract the firmware and examine it using reversing techniques or source code review processes, if available.
Example case
The following screenshot shows the content of the device information file 84:5F:04:F1:45:CA in the /var/lib/bluetooth path of a Linux device, paired with our driver (20:81:9A:10:00:00:00), in which the link key value is found:
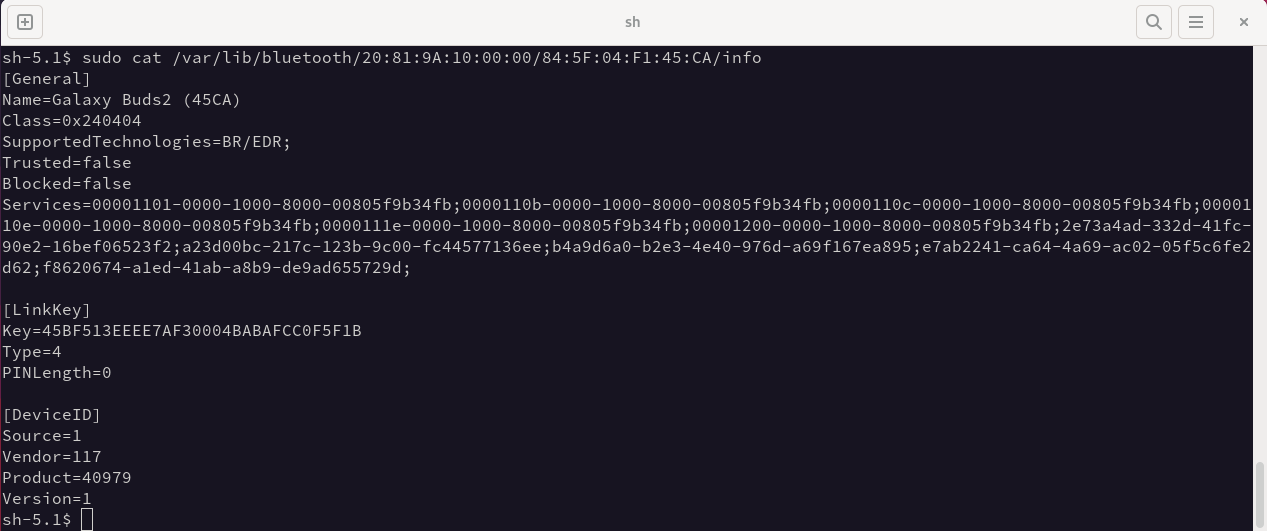
The files are protected by administrator user privileges, but on a device with accessible storage, this information can be extracted. To prevent this, unauthorized access to the storage must be prevented, e.g., by encryption.
