Fight against audiovisual piracy, the challenges
Table of Contents
Combating audiovisual piracy requires continuous investigation into fraudulent activities and the optimization of mechanisms to prevent, detect and respond to them
Almost one in two people in Spain resorts to audiovisual piracy to consume audiovisual content such as films, series or sports broadcasts. This figure is notably higher among citizens under the age of 25. Thus, the latest OTT opinion poll estimates that three out of four young people consume products illegally through downloads and, above all, IPTV services.
What is the most obvious consequence of audiovisual piracy? Millions in economic losses for the various actors that form part of the sector: production companies, distributors, streaming platforms, operators and even sports teams.
In fact, the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) estimates that piracy of sports content alone causes losses of 850 million euros each year in the European Union.
In addition, the EUIPO points out that one in ten young Europeans admits to having bought sports content illegally. This allows us to see the other side of the coin: various actors are enriching themselves illicitly by offering audiovisual piracy services.
How can legal streaming platforms and operators combat audiovisual piracy beyond blocking illegitimate websites?
Inés Cardiel and Jesús Ramírez, cyber intelligence analysts at Tarlogic, presented at RootedCON 2025, the world’s leading Spanish-speaking cybersecurity conference, the results of our company’s research into audiovisual fraud over the last few years.
The experience and expertise accumulated by professionals who provide cyber intelligence services are essential when it comes to helping operators and platforms combat audiovisual piracy, a phenomenon that significantly damages the business model of numerous organizations that generate employment and wealth in our country.
1. An X-ray of the audiovisual piracy ecosystem
The days when users downloaded films or albums using Emule are long gone. Although illegal downloading still exists, audiovisual piracy has been shifting towards models that facilitate the monetization of content theft, such as IPTV lists.
1.1. The consolidation of IPTV lists
This model of audiovisual piracy subverts a legitimate technology such as IPTV to illegally broadcast films, series, television programs and live sports broadcasts. Criminals are thus able to offer users multiple television channels and audiovisual content through a single URL.
As a result, pirate IPTV services are unbeatable in economic terms, marketing annual subscriptions for as little as 50 euros that allow access to LaLiga and Champions League football matches, to watch the NBA or Formula 1 and to consume all kinds of television programs.
1.2. A twist: restreaming services
However, the actors behind pirate IPTV not only market their services directly to users but also sell them to resellers.
Thus, in recent times, restreaming services managed by actors who do not need to have extensive technical knowledge or a powerful technological infrastructure because they do not carry out their management have proliferated.
So what do the resellers do? They act as intermediaries between the pirate service providers and the end consumers. Their role in the audiovisual piracy ecosystem is to market and distribute illegal services.
What are the implications of this criminal business model?
- It enables the entry of players who lack high technical knowledge, thus multiplying the number of criminals who benefit from audiovisual piracy.
- Being freed from the technical management of pirate services, resellers can focus their efforts on optimizing customer acquisition strategies, collection management, or customer service.
1.3. Self-taught learning
Another key phenomenon that has made the ecosystem of audiovisual piracy more dangerous and made it more diverse is the growing trend toward self-teaching.
Thus, various actors decide to set up their pirate service from scratch without resorting to suppliers as resellers do. These actors acquire all the technical and commercial knowledge they need through forums and tutorials.
What are the main consequences of these actors managing their audiovisual piracy infrastructure?
- Actors with more advanced knowledge can configure their servers using the https protocol to obfuscate their infrastructure as much as possible. This makes it difficult to extract the URL of the request containing the domain name of the audiovisual content.
- Having the applications that allow them to have total control of the interface and the functionalities of these applications. This brings four major benefits for criminals:
- Integration of encryption and obfuscation mechanisms to protect URLs.
- Greater freedom to implement changes in the applications and update them according to their business needs.
- Customization of the user experience.
- Direct integration of the application with other internal systems to automate processes such as billing for audiovisual piracy services.
- Implement security protocols and techniques that allow them to evade blockages and make it difficult for cyber-intelligence experts to detect them.
- Adapting to demand, scaling supply, personalizing service and responding quickly to changes in a field as competitive as audiovisual piracy.
1.4. Marketing of pirate services
The experience accumulated by the Tarlogic cyber intelligence team in the investigation and detection of audiovisual piracy shows that the actors market their services through:
- Own websites. These are the criminals’ favorite methods because they:
- Remain open for longer before being detected and blocked.
- Offer a greater reach.
- Provide a higher degree of anonymity.
- Social networks and instant messaging applications. The two platforms most used by audiovisual piracy providers are Telegram and X. Why? The policies of these platforms are less strict than those implemented by Facebook or Instagram with regard to the creation and maintenance of accounts for the commercialization of illicit content. Even so, it is important to point out that on X, profiles that disseminate pirated services are suspended within a few days and that on Telegram, the lifespan of these profiles is longer, but they also end up being blocked.
1.5. Exploitation of vulnerabilities in CDNs
Content delivery networks (CDNs) have become a central element in the functioning of web applications. These networks of servers make it possible to accelerate the loading of all kinds of content and, in particular, of large content such as audiovisual content.
Therefore, CDNs are essential when it comes to ensuring that audiovisual transmissions optimally reach millions of viewers.
From the perspective of malicious actors, CDNs are a priority target for illegitimate access to audiovisual content. For this reason, they are constantly looking for vulnerabilities in CDNs that can be successfully exploited:
- CDN Leeching. This is a technique that allows unauthorized users to access content hosted on a CDN in order to steal a signal and publish it through other means. A very high level of CDN Leeching can mean that twice as many customers are connected to a CDN as have legitimately contracted the audiovisual service.
- Lack of controls to authenticate and authorize requests on the CDN itself.
2. DRM, a key technology for protecting content
When it comes to preventing criminals from exploiting vulnerabilities in CDNs, DRM systems play a fundamental role in facilitating the management of digital rights.
Essentially, we could say that this technology guarantees that only authorized users have access to digital content. In such a way that only a person who has acquired the right to view content can see it.
In addition, DRM seeks to prevent the dissemination of content by preventing it from being downloaded or shared on a screen via a video call while it is being played.
DRM systems must be compatible with the operating systems of the devices from which users access content.
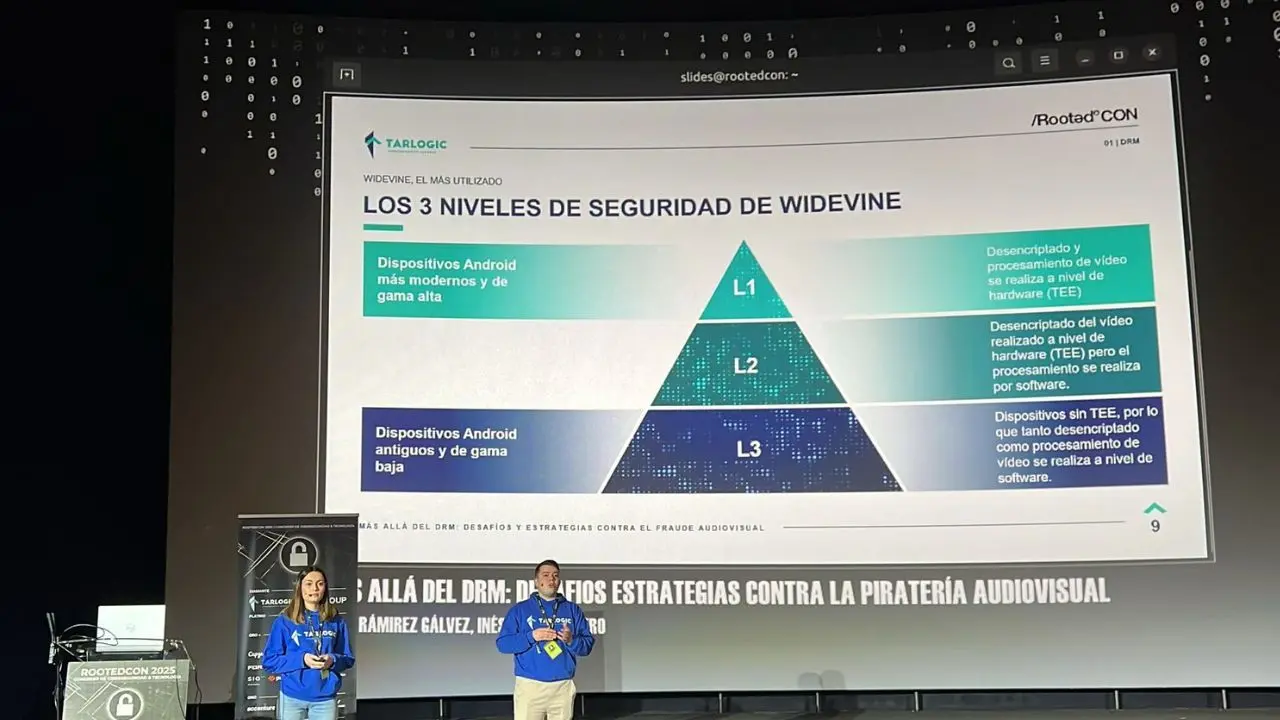
The three main DRM systems on the market are Widevine, developed by Google; Fairplay, owned by Apple; and Playready, by Microsoft. Due to its wide compatibility, Widevine is the most widely used and, therefore, the one most targeted by malicious actors.
Using DRM systems and configuring them properly is essential to protect content from audiovisual piracy. Thus, cyber-intelligence experts recommend:
- Refreshing DRM keys several times a day to view content in order to prevent the dissemination of these keys.
- Block requests are made from certain devices to prevent unauthorized access by malicious actors and the dissemination of content.
3. Continue to strengthen security strategies
In recent years, Tarlogic’s cyber intelligence experts have worked together with legal audiovisual content operators and distributors to combat piracy and improve the resilience of CDNs in the face of criminals’ techniques and tactics.
The strengthening of security strategies has been possible thanks to the implementation of various measures that limit the capacity for the action of pirates.
3.1. Authentication
A key pillar of any security strategy is the implementation of robust authentication mechanisms that ensure that requests for access to content at both the application and CDN levels are authenticated.
3.2. Authorization
Likewise, cyber-intelligence experts recommend deploying authorization mechanisms that allow for continuous and robust authorization control from the CDN to the final application used by users to access content.
3.3. HTTP requests
Another measure that has proven effective is to employ controls at the level of HTTP requests that facilitate the detection of web scraping and illicit codes that pretend to be the real application:
- Limit the use of User-Agents.
- Verify TLS signatures using the JA3 hash. This way, it is possible to find out if a request has been made from a mass-market browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox…) or if, on the contrary, it comes from scraping code or tools. This way, the request can be blocked.
3.4. Monitoring and detection
A key issue in the fight against audiovisual piracy is the continuous monitoring of a provider’s CDN infrastructure. To this end, a system of rules and alerts can be implemented on the connections that reach the CDN. In this way, improper connections that seek to access and distribute audiovisual content illegally can be detected. How?
- By discovering abnormal usage patterns that allow us to block accounts used by audiovisual piracy services to obtain the channels they market through IPTV lists.
- By using controls to detect simultaneous connections to the CDN from a single account.
3.5. Actions against suspicious accounts
Daily work protecting the infrastructures of audiovisual service providers shows that it is necessary to implement measures to curb suspicious accounts:
- Establish a limit for normal use of the services. In such a way that when an account exceeds a maximum threshold of daily viewing hours, it is blocked. This prevents the massive exploitation of CDNs by pirate IPTV services.
- Limit the continuous reproduction of content by means of mechanisms that force the user to refresh the authentication every certain time or to reconnect.
- Implement a system of temporary or permanent bans against suspicious accounts. A measure that is used especially in the video game industry.
4. The importance of cyber intelligence services in the fight against audiovisual piracy
The fight against audiovisual piracy is one of the great challenges of our time. Given its complexity, the EUIPO recommends tackling it from multiple angles. In such a way that the following are combined:
- A regulatory framework that guarantees the rights of operators, streaming platforms, television channels, production companies, sports stakeholders, etc.
- Police operations against large IPTV piracy networks.
- The implementation of awareness campaigns in the educational field so that young people are aware of what it means to subscribe to illicit IPTV lists.
- Continuous research by cyber intelligence professionals to understand the modus operandi of criminals and implement measures that contribute to making CDNs more robust and audiovisual providers more resistant to audiovisual piracy.
Thus, although the blocking of domains and IPs and the conflict between LaLiga and Cloudflare have captured the media’s attention, the truth is that more effective measures are already being implemented to increase the level of protection of audiovisual content.
Cyber intelligence services are critical when it comes to designing, implementing, reviewing and optimizing the security mechanisms of operators and providers.
4.1. Threat Intelligence: A precise overview of the threat landscape
As mentioned above, audiovisual piracy causes millions in losses for many companies and brings criminals a significant amount of profit every year.
This means that those operating in this illegal market have to deal with the continuous optimization of security measures by legitimate content providers, as well as competition from other pirate services.
What are the consequences of this breeding ground? The groups behind the pirated IPTV lists are constantly working to:
- Undermine the security mechanisms of the companies and disseminate audiovisual content illegally.
- Refine their marketing strategy and offer better services than their competitors.
How can companies protect themselves against the most innovative malicious techniques and tactics? Through Threat Intelligence services such as those provided by Tarlogic to industry players, which enable them to:
- Gain precise knowledge of the main threats related to audiovisual piracy.
- Detect potential vulnerabilities and mitigate them so that they are not successfully exploited.
- Adopt measures to prevent audiovisual piracy.
- Having information available to make decisions that combine the business interests of operators and providers with content security.
4.2. Prevention of audiovisual fraud: Combining business and security
In recent years, Tarlogic’s Cyber intelligence division has specialized in fraud investigation and analysis and the fight against audiovisual piracy. The knowledge accumulated by the company’s professionals has allowed us to develop our methodology for:
- Identifying the techniques, tactics and procedures of the actors in the ecosystem of audiovisual piracy and carrying out technical traceability of them.
- Analyzing the fraudulent activities and the technologies used to access and disseminate content illicitly.
- Automating the search for audiovisual piracy services.
- Making estimates of the impact of audiovisual piracy on companies in economic and reputational terms, as well as the consequences of implementing preventive measures against piracy.
- Designing and implementing measures to mitigate the risks and weaknesses that balance security, commercial impact and business vision.
- Supporting the legal strategy of audiovisual providers by capturing evidence and preparing expert reports.
In short, the research presented by Inés Cardiel and Jesús Ramírez, cyber intelligence analysts at Tarlogic, at RootedCON focuses on the challenges in the fight against audiovisual piracy but also on the opportunities facing the players in the sector.
Experience shows that cyber intelligence services play a critical role in strengthening security strategies and continuously optimizing content protection measures against piracy.
Eradicating audiovisual piracy 100% is a pipe dream because, as in any other digital environment, there is no such thing as total security.
However, operators and providers are already implementing effective mechanisms and measures to prevent the actors behind fraudulent services from illegitimately accessing and disseminating audiovisual content.